LearnBN on Nostr: 7. Reclaiming Disk Space ...
7. Reclaiming Disk Space
เมื่อธุรกรรมถูกบรรจุลงในบล๊อกแล้ว สามารถกำจัดธุรกรรมที่ใช้ไปแล้วก่อนหน้านั้นออกได้เพื่อประหยัดพื้นที่ดิสก์ แต่การจะทำอย่างนี้ได้โดยไม่ให้เลข hash ของบล๊อกมีการเปลี่ยนแปลงนั้น ธุรกรรมจึงจำเป็นต้องถูก hash ในรูปแบบของ Merkle Tree [7][2][5] โดยมีแค่ root node ของ tree เท่านั้นที่จะรวมอยู่ใน hash ของบล๊อก นี่เป็นวิธีที่ทำให้สามารถบีบอัดข้อมูลในบล๊อกเก่า ๆ ได้โดยการตัดพวก hash ส่วนอื่น ๆ ของ tree ที่ไม่ใช่ root node ออก (ไม่จำเป็นต้องเก็บ hash ในชั้นอื่น ๆ ของ tree)
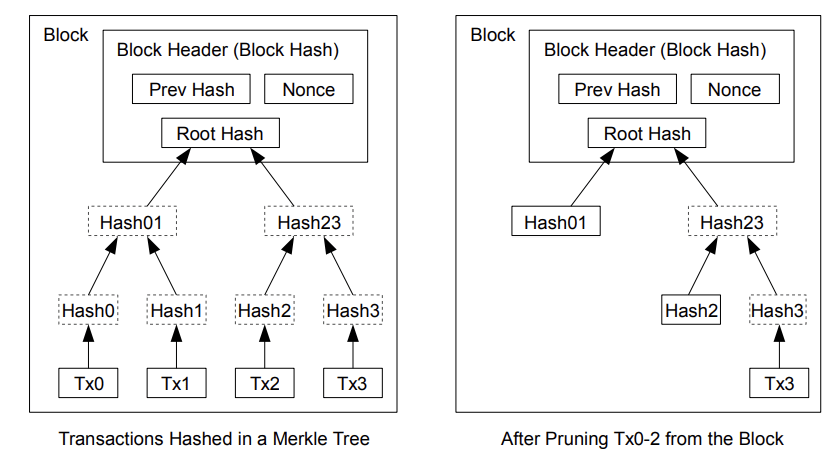
โดยในส่วน header ของบล็อกที่ไม่มีธุรกรรมจะมีขนาดประมาณ 80 ไบต์ หากเราสมมติว่าบล็อกถูกสร้างขึ้นทุก ๆ 10 นาที 80 ไบต์ * 6 * 24 * 365 = 4.2MB ต่อปี โดยที่ระบบคอมพิวเตอร์ทั่วไปที่วางขายในปี 2551 มี RAM 2GB และกฎของมัวร์ทำนายการเติบโตในปัจจุบันที่ 1.2GB ต่อปี การจัดเก็บข้อมูลไม่น่าจะเป็นปัญหาแม้ว่าส่วนหัวของบล็อกจะต้องถูกเก็บไว้ในหน่วยความจำก็ตาม
#siamstr
[2] H. Massias, X.S. Avila, and J.-J. Quisquater, "Design of a secure timestamping service with minimal
trust requirements," In 20th Symposium on Information Theory in the Benelux, May 1999.
[5] S. Haber, W.S. Stornetta, "Secure names for bit-strings," In Proceedings of the 4th ACM Conference
[7] R.C. Merkle, "Protocols for public key cryptosystems," In Proc. 1980 Symposium on Security and
Privacy, IEEE Computer Society, pages 122-133, April 1980.
Published at
2024-08-01 11:43:31Event JSON
{
"id": "0000023de1e42be305ff11ec5474cb0e53f6b6e0f379b362204dd9f23ddab1f5",
"pubkey": "79008e781adec767cc8e239b533edcb19ea2e260f9281a9125e93425dfac9395",
"created_at": 1722512611,
"kind": 1,
"tags": [
[
"t",
"siamstr"
],
[
"nonce",
"528634",
"21"
]
],
"content": "7. Reclaiming Disk Space\n\nเมื่อธุรกรรมถูกบรรจุลงในบล๊อกแล้ว สามารถกำจัดธุรกรรมที่ใช้ไปแล้วก่อนหน้านั้นออกได้เพื่อประหยัดพื้นที่ดิสก์ แต่การจะทำอย่างนี้ได้โดยไม่ให้เลข hash ของบล๊อกมีการเปลี่ยนแปลงนั้น ธุรกรรมจึงจำเป็นต้องถูก hash ในรูปแบบของ Merkle Tree [7][2][5] โดยมีแค่ root node ของ tree เท่านั้นที่จะรวมอยู่ใน hash ของบล๊อก นี่เป็นวิธีที่ทำให้สามารถบีบอัดข้อมูลในบล๊อกเก่า ๆ ได้โดยการตัดพวก hash ส่วนอื่น ๆ ของ tree ที่ไม่ใช่ root node ออก (ไม่จำเป็นต้องเก็บ hash ในชั้นอื่น ๆ ของ tree)\n\nhttps://image.nostr.build/3ed95334891d91baca3f3f6f624a7ae22620be4ebfe0db5eb652cfce11255b9a.png\n\nโดยในส่วน header ของบล็อกที่ไม่มีธุรกรรมจะมีขนาดประมาณ 80 ไบต์ หากเราสมมติว่าบล็อกถูกสร้างขึ้นทุก ๆ 10 นาที 80 ไบต์ * 6 * 24 * 365 = 4.2MB ต่อปี โดยที่ระบบคอมพิวเตอร์ทั่วไปที่วางขายในปี 2551 มี RAM 2GB และกฎของมัวร์ทำนายการเติบโตในปัจจุบันที่ 1.2GB ต่อปี การจัดเก็บข้อมูลไม่น่าจะเป็นปัญหาแม้ว่าส่วนหัวของบล็อกจะต้องถูกเก็บไว้ในหน่วยความจำก็ตาม\n\n#siamstr\n\n[2] H. Massias, X.S. Avila, and J.-J. Quisquater, \"Design of a secure timestamping service with minimal\ntrust requirements,\" In 20th Symposium on Information Theory in the Benelux, May 1999.\n[5] S. Haber, W.S. Stornetta, \"Secure names for bit-strings,\" In Proceedings of the 4th ACM Conference\n[7] R.C. Merkle, \"Protocols for public key cryptosystems,\" In Proc. 1980 Symposium on Security and\nPrivacy, IEEE Computer Society, pages 122-133, April 1980.",
"sig": "109938b6e94af456bfe1710a192dc2b503e6e04cb4891eb5fbaa5d45a180d8dde13c9080dfe8efb1a17cd12951f155e1b6cb90293246b50ee8fa4ca53f9079bd"
}

